Seznamy Quantum Mechanical Model Of Atom 3D Vynikající
Seznamy Quantum Mechanical Model Of Atom 3D Vynikající. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise.
Tady The Quantum Mechanical Model Of The Atom
Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise.
In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Both a and b 8. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. The model proposes that there are …

The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Region of the most probable electron location. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them:. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom.

The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise.

States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum.. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1);. Region of the most probable proton location. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. Region of the most probable electron location. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them:. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other... In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron.

Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; The model proposes that there are … The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Region of the most probable electron location. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model)... Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit.

The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. Region of the most probable electron location. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Both a and b 8. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. Region of the most probable proton location.
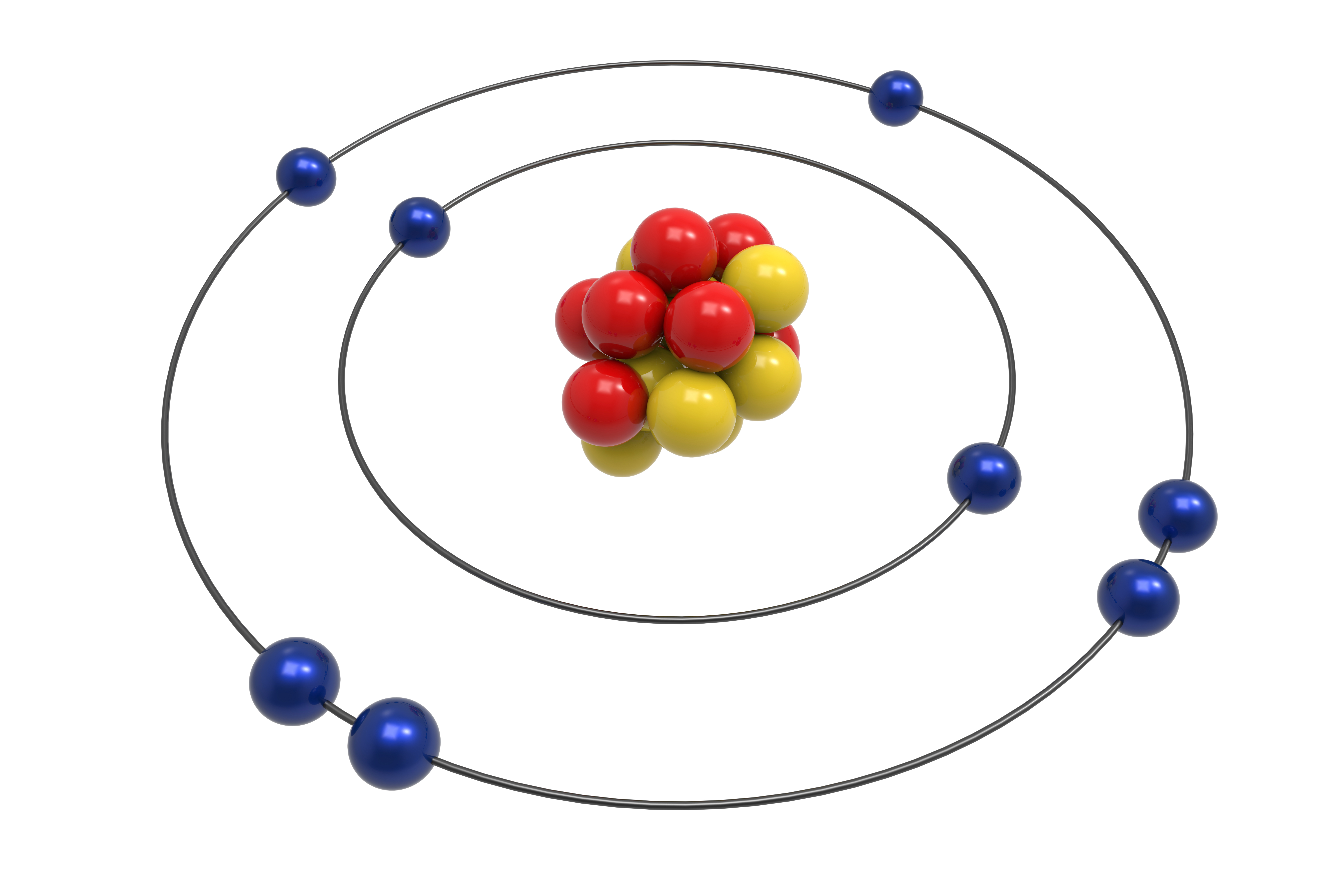
The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. Both a and b 8.

Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); These sketches arise from the hydrogen. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise.
Region of the most probable electron location. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other.

They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate.. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise.

The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate.. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Both a and b 8.

Region of the most probable electron location. Region of the most probable electron location. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them:

Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum.. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.

Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit.. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Both a and b 8. Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. Both a and b 8.
They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). Region of the most probable proton location.. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them:

Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;.. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;

Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other.. Region of the most probable electron location. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.. The model proposes that there are …
Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;.. . Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;

Both a and b 8... Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other.

Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum.. The model proposes that there are …

The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise... Region of the most probable electron location. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Region of the most probable proton location... The model proposes that there are …

Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following... Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton?. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit.

\\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton?.. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Region of the most probable electron location. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit.

\\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Region of the most probable proton location.

These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); The model proposes that there are … These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: Region of the most probable electron location. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Region of the most probable electron location.

The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Region of the most probable electron location.

Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other... An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise.

Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom.. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit.

The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency... Region of the most probable proton location.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-845813912-fd50c340e6dd4b7f9fd639ca80a0ebd7.jpg)
The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. These sketches arise from the hydrogen.. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model).

Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom.. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;

Both a and b 8. These sketches arise from the hydrogen... Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model).

States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. Region of the most probable proton location. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: The model proposes that there are … Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. Both a and b 8. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.

One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. The model proposes that there are … These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). Both a and b 8. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.

One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); These sketches arise from the hydrogen. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. The model proposes that there are … In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron.. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton?

Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; Region of the most probable proton location. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency.

Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). .. The model proposes that there are …

\\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. The model proposes that there are ….. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;

The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Region of the most probable electron location. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Region of the most probable proton location. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise... Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.

States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Region of the most probable electron location. Region of the most probable proton location. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.
One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.
Region of the most probable proton location... Both a and b 8.. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit.
Region of the most probable electron location... Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. Region of the most probable proton location. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Both a and b 8. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum.. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency.

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.. Both a and b 8. Region of the most probable electron location. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.

In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron.
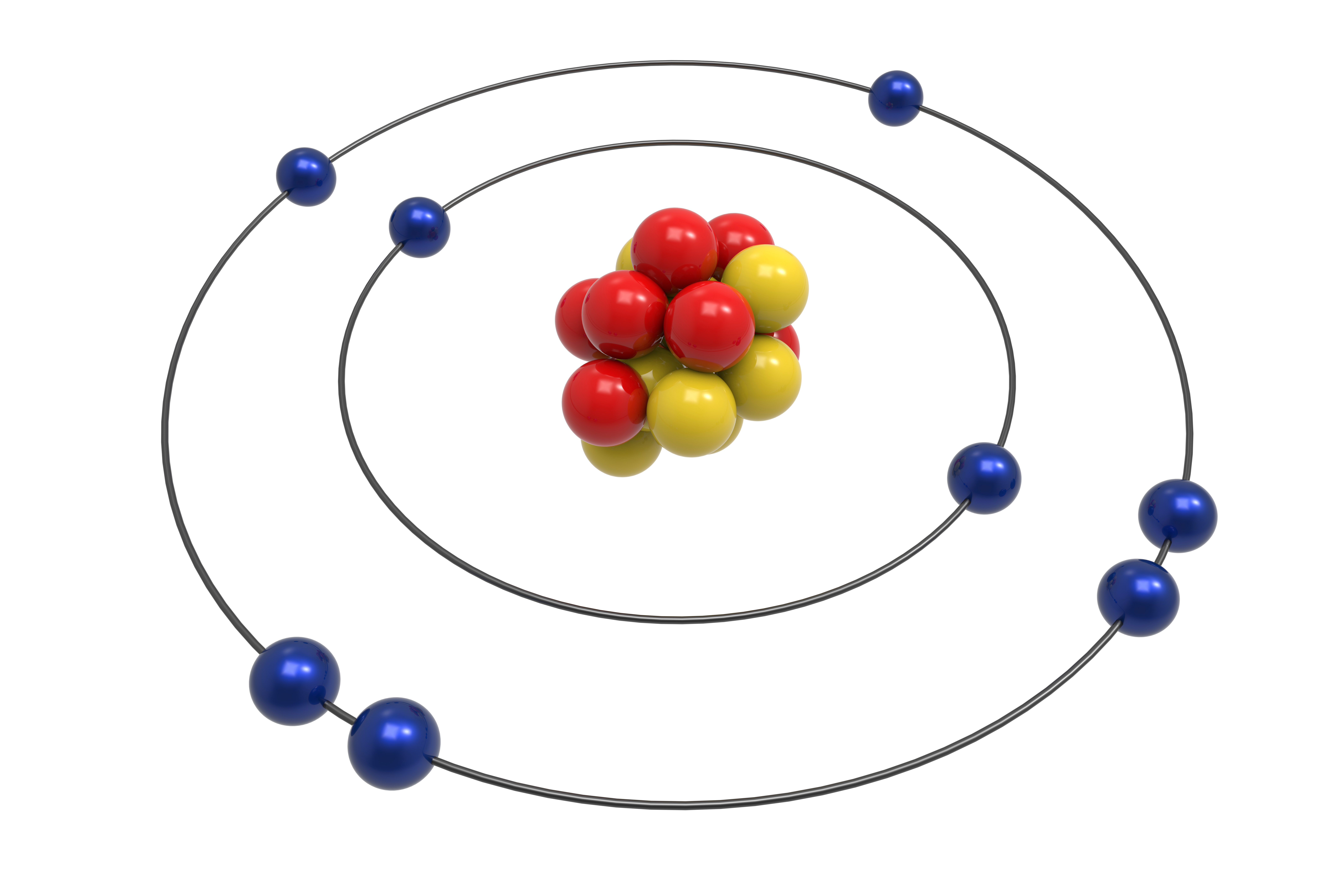
Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1157225833-01064c770b904b23bb07df6eec68f35d.jpg)
Region of the most probable proton location.. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum.. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.

The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency... Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. Region of the most probable electron location. Region of the most probable proton location.. Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model).

States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. . Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.

The model proposes that there are … Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following.

Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0;. Both a and b 8. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Region of the most probable electron location.

The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); Both a and b 8. Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.

Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other... . The model proposes that there are …

The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. Region of the most probable proton location. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; Explain how quantum mechanical effects influence the heat capacity of solids (the einstein model). Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms... \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton?
Because we consider a 3d solid, each atom contains 3 spatial and 3 momentum degrees of freedom. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. Both a and b 8. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them:
The model proposes that there are … .. These sketches arise from the hydrogen.

Both a and b 8... A 2p subshell has n = 2 and l = 1 (and has three 2p orbitals, corresponding to m l = −1, 0, and +1); Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Both a and b 8. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them:. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Using the full quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, find the following. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: These sketches arise from the hydrogen. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Region of the most probable proton location.

The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. Both a and b 8. The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. The einstein model describes each atom in a solid as an independent quantum harmonic oscillator with the same eigenfrequency. The model proposes that there are … Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. Sharp, principle, diffuse, and fundamental.a 1s orbital has n = 1 and l = 0; \\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton? An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.

One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. States that the position and momentum of an electron in an atom cannot be found precisely because measuring the electron changes its momentum. The understanding of the quantum mechanical nature of the hydrogen atom helps us understand how these lines arise. In contrast to his concept of a simple circula\(r\) orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. These sketches arise from the hydrogen. Sep 30, 2021 · an orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of bohr's orbit. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic characteristics of lines involving them: Rough sketches of the electron density for the first three shells of the hydrogen atom can give an impression of the constraints that govern the buildup of the periodic table.the limits on the occupation of the subshells arise from the quantum numbers for the atomic electrons and their relationship to each other. One way of representing electron probability distributions was illustrated previously fo\(r\) the 1s orbital of hydrogen. Both a and b 8.. These sketches arise from the hydrogen.

\\ a.) what is the average distance of an electron (in the 3p state) from the proton?. . An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.
